Difference between alkyl and aryl.
Alkyl aryl vinyl difference.
Vinylic carbocations are unstable as compare to the allyl carbocations as they lack p character.
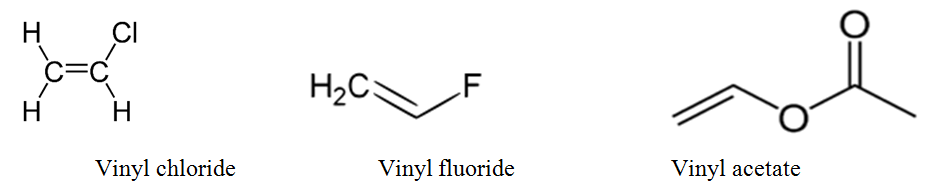
A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom vinyl chloride h 2c chcl is an example.
The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
In vinyl group c c is directly attached to the rest of the chain.
Noun chemistry uncountable the univalent radical ch 2 ch derived from ethylene countable any of various compounds and substances containing the vinyl radical especially various tough flexible shiny plastics.
Alkyl and aryl are two chemical terms used to name functional groups of organic compounds.
Vinyl contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
Vinyl indicates the ch ch 2 functional group which can be formed by removing hydrogen from ethylene.
As nouns the difference between aryl and vinyl is that aryl is.
Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.
Functional groups are parts of organic molecules having the responsibility for the characteristic properties of a certain molecule.
Alkyl groups and aryl groups are two examples of functional groups.
An alkyl group is a functional group that can be.
Alkyl anagrams vinyl.
They are moieties of large molecules.
With the exception of hf pk a 3 2 all the hydrohalic acids are very strong small differences being in the direction hcl hbr hi.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
The vinyl compounds are every reactive and they polymerize to form the vinyl polymers as in the case of polyvinyl acetate polyvinyl chloride and polyvinyl fluoride.
This is the main difference between allyl and vinyl groups.
However alkyl halides may sometimes be confused with aryl halides.
Main difference alkyl vs aryl.
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds.
Both alkyl and aryl groups have carbon and hydrogen atoms.
For example if the halogen atom is attached to a carbon atom which is attached to a benzene ring cl ch 2 c 6 h 5 one would think it is an aryl halide but it is an alkyl halide because the halogen atom is attached to the carbon that is sp 3 hybridized.
In contrast to vinyl allyl group is attached to the rest of the molecule through ch 2 group.
An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring.
The characteristics noted above lead us to anticipate certain types of reactions that are likely to occur with alkyl halides.